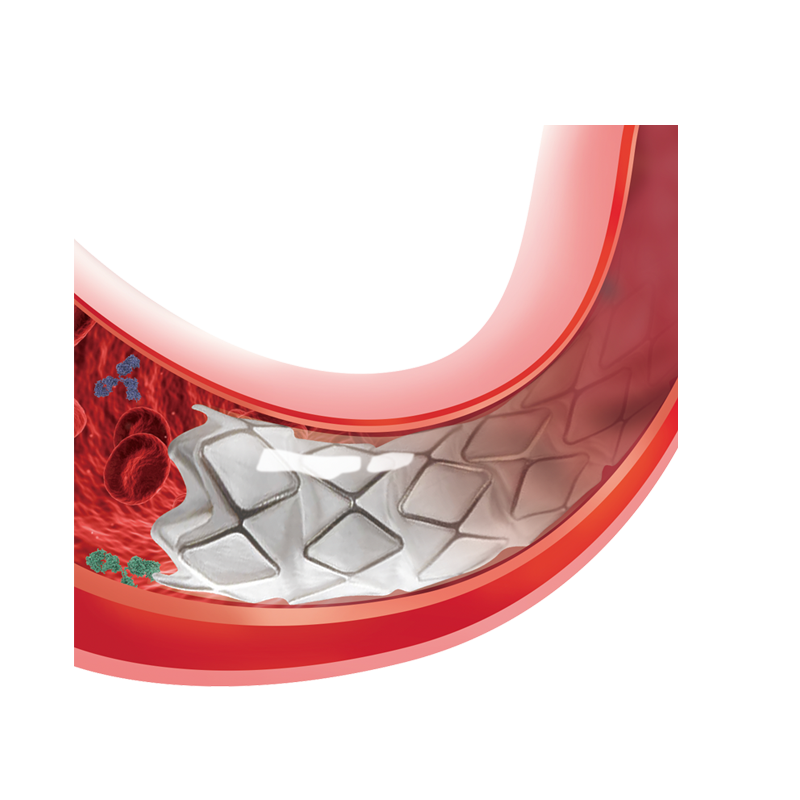
Product Introduction
Main Component Introduction – Biomimetic Phospholipid
The primary ingredient of the jHemo PC® Phosphorylcholine Hemocompatible Coating is phosphorylcholine (PC), the main lipid found on the outer layer of non-activated cell membranes. As an amphiphilic phospholipid (hydrophilic and lipophilic), it naturally resists protein and cell adhesion, forming an effective biomimetic coating for functional medical device coatings.
Covalent Bonding for Stability
PC is covalently bonded to the surface of medical devices, creating a stable phosphorylcholine surface coating. This bonding significantly reduces thrombosis caused by protein aggregation, acting as a reliable antithrombogenic coating for catheters and vascular access device coatings.
Water Layer Protection – Anti-Adhesion & Anti-Crystallization
The PC-containing material is surrounded by water molecules, which effectively cover the substrate. This layer forms a biological “non-stick” surface that resists protein and cell adhesion, providing a hemocompatible coating. It also functions as an anti-adhesive and anti-crystallization layer, maintaining the integrity and performance of catheter coatings over time.
Key Features
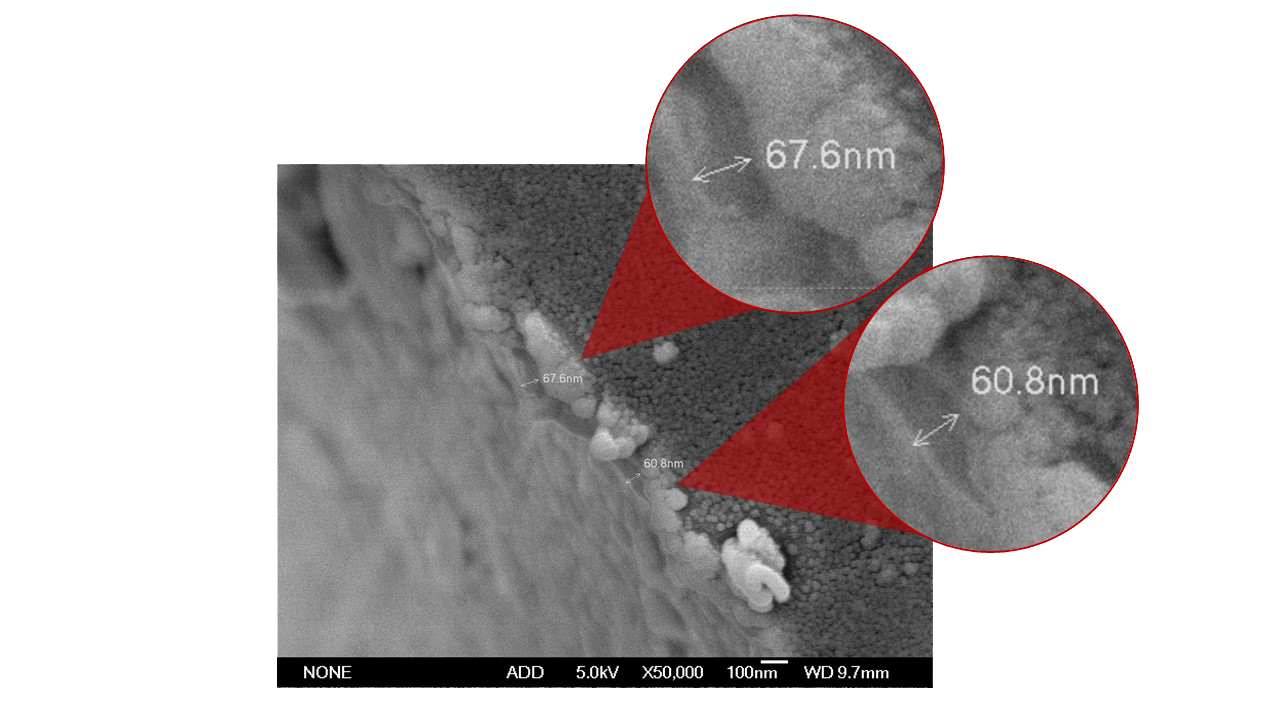

1.Biomimetic Material Composition
▷ The main component is phosphorylcholine (PC), the predominant lipid in the outer layer of non-activated cell membranes.
▷ As an amphiphilic phospholipid (hydrophilic and lipophilic), PC naturally resists protein and cell adhesion, providing a foundation for an effective hemocompatible coating.
2.Covalent Surface Bonding
▷ PC is covalently bonded to device surfaces, forming a stable phosphorylcholine surface coating that reduces thrombosis caused by protein aggregation.
▷ Acts as an antithrombogenic coating, preventing clot formation and improving patient safety.
3.Ultra-Thin, Drug-Free Layer
▷ Achieves nanometer-level coating thickness, maintaining the device’s functional dimensions.
▷ Free of drugs, minimizing inflammatory responses and ensuring compatibility with sensitive vascular access and catheter applications.
4.Anti-Adhesion and Anti-Crystallization Properties
▷ Water molecules surrounding PC create a biological “non-stick” surface.
▷ Effectively resists protein and cell adhesion while inhibiting crystallization, enhancing long-term performance.
5.Simple and Versatile Application
▷ The coating process is straightforward and adaptable to various catheter coating and vascular access device coating applications.
▷ Compatible with a wide range of substrates used in medical device manufacturing.
Application product
Trusted Antithrombogenic Coating for Medical Devices
jMedtech’s Phosphorylcholine coating delivers reliable hemocompatible coating solutions across 10+ medical device applications. Our functional medical device coatings and biomimetic coating technologies ensure excellent anti-coagulative performance for catheter coatings and vascular access device coatings. Trusted by partners worldwide, jMedtech continues to advance phosphorylcholine surface coating innovation.
Not sure if Phosphorylcholine coating suits your business? Contact our experts for guidance.
Stent grafts
Metal implants
Introducer sheaths
Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
Heart valves
Vascular grafts
Neurological guidewires and catheters
Haemodialysis catheters
Embolic protection devices
Vena cava filters
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
Others
Performance Tests
We have done a series of tests on jHemo PC® Phosphorylcholine Anticoagulant Coating, the following is the result of a comparative test.
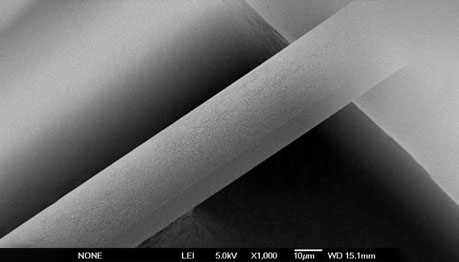 Uncoated stent surface - 1000x
Uncoated stent surface - 1000x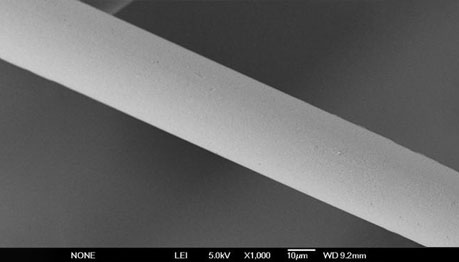 PC-coated stent surface - 1000x
PC-coated stent surface - 1000x

 No Coating
No Coating With Coating
With Coating

 No Coating
No Coating With Coating
With Coating

 No Coating
No Coating With Coating
With Coating

 No Coating
No Coating With Coating
With Coating
Technical Resources
Download more information on how our jHemo PC® Phosphorylcholine Hemocompatible Coating and expertise can tackle unmet needs.