For medical devices such as catheters and stents implanted in the human body, the hydrophilic coating on the surface can reduce the patient's discomfort, pain and tissue damage when entering the human body.
The FDA's introduction to the function of medical hydrophilic coatings is: "Medical devices such as intravascular catheters, guide wires, balloon catheters, delivery sheaths, and implant delivery systems are commonly used in microvascular, cardiovascular, and peripheral vascular systems. For invasive diagnosis and treatment procedures, the surface of these devices usually has a hydrophilic coating (for example, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), polytetrafluoroethylene, silicone) to reduce friction between the device and human tissue. These coatings can provide doctors with Greater maneuverability, and potentially less trauma to the patient's blood vessels."
In recent years, domestic and foreign coating manufacturers have been exploring methods for evaluating the performance of hydrophilic coatings, so that relevant medical devices and clinics can fully trust and apply them. To evaluate the performance of the hydrophilic layer, in addition to testing its lubricity, it also includes testing the uniformity, service life and stability of the coating.
Brighton Science conducts research on medical hydrophilic coatings and proposes the following evaluation directions:
As part of a medical device, in order to test the reliability of the hydrophilic coating, it can be tested:
1. Biocompatibility of manufacturing materials
2. Sterility of any material that will come into contact with the patient
3. Pyrogenicity, to observe the level of endotoxin and other pyrogens on the surface of materials that may cause infection in patients
4. Packaging and storage shelf life, to ensure that the sealed medical device maintains performance and sterility within the usable period
5. Conduct non-clinical tests on the tensile strength, size verification and kink resistance of the guide wire to ensure that the guide wire will not bend and kink during use.
In addition to the above general test items for medical devices, there are also test items that should be set for the characteristics of medical coatings.
Any device material implanted in the human body should have specifications to ensure that it will not cause infection, cause excessive discomfort or pain to the patient, and will not cause performance failure due to corrosion or loss. Therefore, it should be checked whether the binding strength of the hydrophilic coating to the surface, that is, the stability of the coating, meets the requirements for clinical use.
Coating detachment can have very serious consequences, as stated by the FDA: "Coating detachment, i.e. flaking, detachment, degradation, may adversely affect clinical presentation (e.g., lead to entry site inflammation, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, myocardial infarction) embolism, myocardial infarction, embolic stroke, cerebral infarction, delamination and/or detachment of tissue necrosis) or death.”
The main factors affecting the stability of the coating are as follows:
1. The composition of the coating
2. Curing of the coating
3. The quality of the coating
When these factors are controlled, and production level verification is performed during the study, it can be ensured that the catheter coating produced meets the requirements.
The catheter is submerged in a solution containing the radioactive compound, and the amount of radioactive compound adhered to the catheter is measured. This method of measurement simulates the principle of blood coagulation in the body. Fibrinogen is produced by the liver and released into the blood to cause coagulation. A high count of adhered radioactive substances indicates that more coagulation has occurred on the surface of the catheter, that is, the coating is not lubricated enough. .
The contact angle can indicate the wettability of the surface of the object, which is also a way to show the hydrophilicity of the test catheter. The smaller the measured contact angle, the greater the wettability and the better the hydrophilicity.
When the contact angle is inconsistent across the catheter surface, it is an indication that the coating may not have been applied evenly. For a catheter with good hydrophilic properties, the liquid drop on its surface should wet the entire surface evenly, and the contact angle should be consistent.
One of the most important properties of medical device coatings for human interventional therapy is the hydrophilicity of the coating. Hydrophilic coatings have extremely low or zero contact angles because the liquid spreads completely on the surface and glides off immediately. This smooth quality allows blood that comes into contact with the catheters to flow right around them without any hindrance.
The purpose of using a hydrophilic coating is to reduce the surface friction of the catheter, facilitate insertion during surgery, and prevent it from causing the surrounding blood to coagulate. Therefore, the lubricity of hydrophilic coatings is extremely important for medical catheters. To detect the lubricity of the coating, generally, the hydrophilic coating catheter is clamped and pulled, and the friction value is obtained by measuring the structure, and the lubricity is judged by the friction.
The hydrophilic coating formula developed and produced by jMedtech Coating is safe, has good biocompatibility, balance between lubricity and firmness, low graininess, and good flexibility, which can improve the safety and comfort of interventional catheters. Focusing on the research and development and production of medical coatings for 10 years, it has won clinical trust, served more than 500 medical device companies and groups, and is a long-term partner of many listed companies.
The figure below is a comparison chart of the friction coefficient of the guide wire before and after being coated with special hydrophilic coating for jMedtech metal:
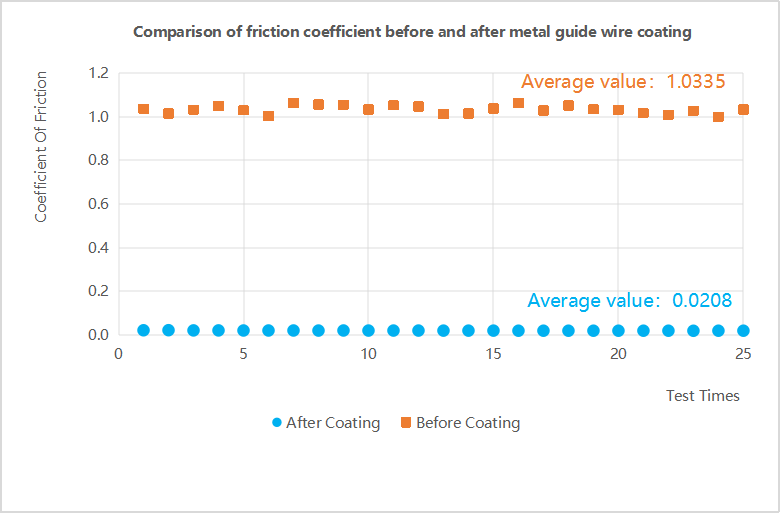
Observing the chart, it can be seen that the coating of jMedtech coating on the surface of the guide wire can reduce its surface friction by more than 95% to achieve a super lubricating effect; the friction coefficient of the guide wire after coating remains stable in 25 tests, It shows that the firmness and stability between the coating and the guide wire are high.
The friction data is detected by the friction testing equipment independently developed and produced by jMedtech. The key components of the equipment are all imported high-end brands, with ultra-high-precision controllers, the Windows system is easy to operate, and the test results are automatically generated. time and energy, improve work efficiency.